With the rise of cyber threats, organizations are now encouraged to invest in robust security measures, not only to meet compliance requirements, but also to adapt to new requirements from insurers.
Thus, organizations are beginning to align their cybersecurity efforts with their insurance policies to try to obtain more favorable insurance rates, reflecting a paradigm shift where cybersecurity measures directly influence insurance premiums.
The cybersecurity insurance market has reached a level of maturity such that applicants and providers of cyber insurance have acquired precise knowledge of how threats translate into claims and generally understand the need for minimal security controls to help prevent and mitigate the effects of these threats.
As they seek to protect themselves from the financial consequences of cyberattacks, organizations face a dual challenge: an increase in cybersecurity insurance costs and a decrease in the coverage offered.
This trend highlights the growing need for organizations to improve their own security measures and rigorously evaluate their suppliers.
Cybersecurity insurance, more popular than ever despite increasing costs.
Despite the increase in costs and the complexity of cyber threats, the demand for cybersecurity insurance continues to increase. Companies of all sizes are increasingly investing in cybersecurity insurance policies to protect themselves against the financial consequences of data breaches, ransomware, and other types of cybersecurity incidents.
The demand for these insurances is also driven by the evolution of government regulations and compliance requirements, prompting companies to seek suitable insurance coverage.
The global market for cybersecurity insurance is expected to be worth nearly 90 billion euros in 2033, with an annual growth rate of nearly 22.3% between 2024 and 2033. In 2023, its value is expected to exceed 12 billion euros.
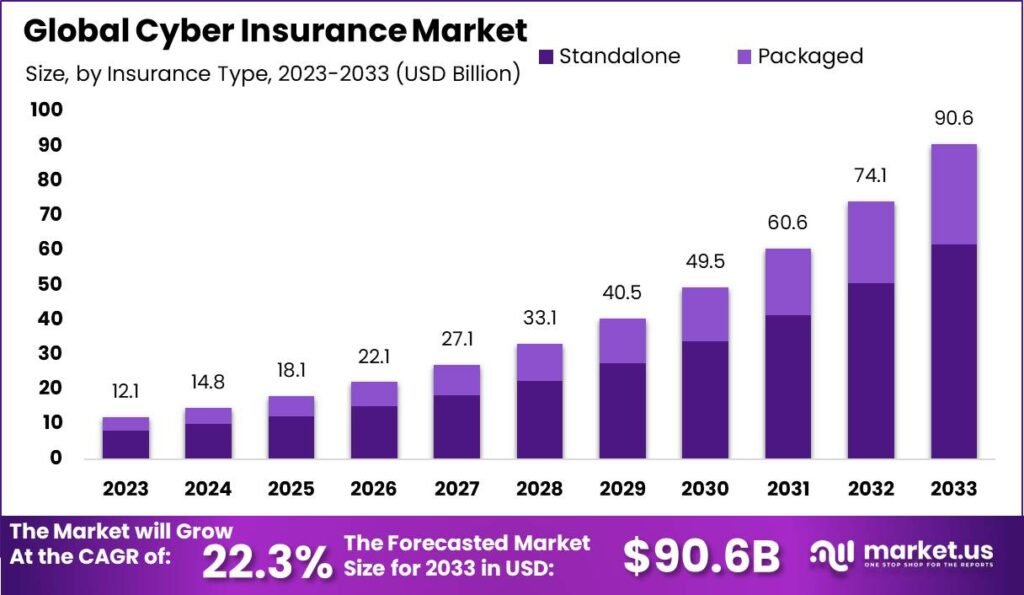
Source: market.us.
The maximum coverage amounts of cyber insurance providers are highly variable, ranging from 1 million euros to 100 million euros per claim.
Faced with a series of massive data breaches, the insurance industry is forced to revise its rates upwards while limiting the scope of its coverage. This evolution is partly due to reduced visibility of risks compared to other insurance sectors, as well as a significant increase in claims.
Third-party coverage at the heart of market concerns
Third-party coverage holds a significant share of more than 62% in the insurance market, highlighting the importance of protecting businesses against third-party claims resulting from data breaches or cybersecurity incidents.
For more details on market data, we invite you to consult the market.us website here. and the Media article.
The rise of automated vendor assessments
With the consolidation of the supply chain and the increasing complexity of security ecosystems, automated vendor assessments are becoming essential. These assessments allow for more effective and comprehensive management of third-party security risks.
Automated vendor assessments, offered by platforms such as SecurityScorecard, Findings.co, and Scytale.ai, provide effective and cost-efficient solutions for assessing and managing third-party risks, thus ensuring compliance with cybersecurity insurance requirements.
🛡️ SecurityScorecard: This platform offers technologies such as automated cybersecurity questionnaires and security rating systems to build a comprehensive vendor risk management program. These tools help mitigate risks and streamline processes while improving speed and reducing the work required for effective third-party risk management. For more information, you can visit the SecurityScorecard website.
🤖 AssessmentAI: This is an automated auditor powered by generative AI that integrates AI into security assessment and audit processes. It improves efficiency and responsiveness, offering a faster, clearer, and simpler experience for both suppliers and companies. AssessmentAI optimizes supply chain risk management and significantly reduces supplier audit costs. For more information, you can visit the Findings.co website.
🌐Scytale.ai: This platform focuses on operational cost savings through automation. It offers intuitive tools and automated workflows for quick supplier evaluation and risk identification, leading to operational efficiencies and cost reductions. For more information, you can visit the Scytale.ai website.
These platforms offer effective and cost-efficient solutions for evaluating and managing third-party risks, thus ensuring compliance with the changing requirements of cybersecurity insurance.
The main requirements of insurers in terms of cybersecurity
Modern Attack Surface Management (ASM)
In the United States, SEC Rule 106, announced last July, imposes new obligations for publicly traded companies to quickly disclose incidents and report annually on cybersecurity risk management, strategy, and governance.
Modern Attack Surface Management (ASM) is becoming a key requirement in cybersecurity insurance. Modern ASM offers the visibility and monitoring necessary to comply with this rule while meeting insurers’ expectations.
Implementation of an XDR Solution (Extended Detection and Response)
Insurers favor organizations with XDR solutions for several key reasons. XDR solutions offer extended visibility and continuous monitoring, crucial for compliance with regulations such as SEC Rule 106. These solutions integrate and manage security across all devices, accounts, and applications, providing continuous rather than periodic risk assessment. This comprehensive approach allows security teams to quickly identify and respond to threats, thereby reducing overall risk and making the organization more attractive to insurers. Additionally, the intelligent analytics capabilities of XDR solutions help organizations effectively prioritize risks, accelerating mitigation and supporting a proactive cybersecurity posture.
Prioritization of Vulnerability Management
Insurance underwriters will focus on vulnerabilities they consider most critical and exploitable, and heavily incorporate them into their risk assessments.
Exclusion of Manufacturing Breaches from Insurance Coverage
The digitization within Industry 4.0 has increased risks for industrial environments, leading many industrial companies to turn to cybersecurity insurance. However, insurers might no longer cover damages suffered by these organizations.
The manufacturing industry is critical, vital to the economy. An attack against a manufacturer may aim not to harm a specific company but to disrupt the economy. In such situations – especially if several manufacturers are affected simultaneously – insurers might consider the attacks as acts of war rather than cybercrimes, and acts of war are excluded from coverage.
Effectiveness of Incident Response (IR) Plans
Insurance companies are likely to require documented and tested incident response plans as a mandatory requirement of cybersecurity insurance. The same requirement is found in the new European NIS2 Directive 🔍 which is expected to set the tone for 2024. Effective as of January 2023, it will be implemented from October 2024 (the NIS2 Directive by ANSSI).
Implementation of Managed Security Services (Managed Security Services Provider – MSSP)
Insurers favor organizations with managed security services for several essential reasons. Firstly, MSSPs offer cybersecurity expertise that may be lacking internally in many organizations. This expertise is crucial to face increasingly sophisticated cyber threats and maintain a robust security posture.
MSSPs provide services such as continuous security event monitoring, managed threat detection and response, penetration testing, and proactive threat hunting, thus ensuring comprehensive protection.
Additionally, MSSPs can help manage and efficiently allocate security budgets, thereby reducing overall cybersecurity costs for organizations. They also offer compliance administration, which is essential to meet regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. This compliance is an important factor for insurers when evaluating risk and insurance coverage.
Moreover, MSSPs consolidate experienced professionals in a high-demand field, allowing for the centralization of limited cybersecurity resources to provide optimal service. This is particularly beneficial for organizations that cannot afford to develop a robust internal security team. Outsourcing security maintenance and monitoring to an MSSP allows organizations to benefit from enhanced protection while focusing on their core business objectives.
In summary, the use of MSSPs can increase the quality of protection, improve accurate threat detection, and assist with regulatory compliance, which is favorable in the eyes of insurers. Organizations using managed security services are often better prepared and equipped to meet the increasing demands of insurers in cybersecurity.
This article underscores the growing importance of adapting to the evolving cybersecurity insurance market. Organizations must now contend with increased costs and reduced coverage, while meeting compliance requirements and insurers’ expectations. The rise of automated vendor assessments and the adoption of more comprehensive cybersecurity strategies, including modern Attack Surface Management (ASM) and the implementation of XDR solutions, become crucial. Furthermore, the growing importance of third-party coverage and the emergence of managed security services (MSSP) reflect a trend towards more proactive and strategic risk management in cybersecurity. This approach is expected to become the norm, especially in sectors like insurance. In this era of digital transformation, it’s more important than ever for companies of all sizes to invest in robust security measures and stay informed about the best practices and solutions available to protect their digital assets and maintain competitiveness in the market.

